Water Parameter
Measurement of water parameter
Water quality is a critical factor when culturing any aquatic organism. Optimal water quality varies by species and must be monitored to ensure maximum growth rate and survival. This is specifically true for an indoor hatchery but also for pond systems where larvae and fry are produced. Larvae and fry are quite sensitive concerning the water parameter and need a specifically careful monitoring.
The quality of the water in the production systems can significantly affect the organism's health. Water quality parameters that are commonly monitored in the aquaculture industry include temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, alkalinity, hardness, ammonia, nitrite and nitrate. Depending on the culture system, carbon dioxide, chlorides, and salinity may also be monitored. Some parameters such as alkalinity and hardness are fairly stable, but others like dissolved oxygen and pH may fluctuate daily.
It is important to establish a standardized water quality testing protocol for your particular situation. Know the tolerance range for your culture species, establish critical levels, and be prepared to act if a problem occurs. The Table 5 below indicates the water quality preferences for some commonly cultured species.
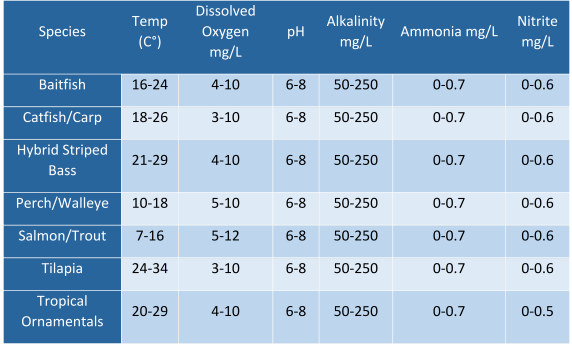
The table provides some examples of recommended water parameter for
various fish species. The oxygen saturation is a relative measure
of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved in water as a
proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in
that medium. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such
as an oxygen. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%).
Please note: the higher the water temperature, the lower is the
amount of dissolved oxygen to achieve a
 saturation of 100%.
saturation of 100%.
Special care is needed with the monitoring of Ammonium. Please note, that the most toxic form of ammonium (NH3 ) increases significantly with increasing pH (acidity or alkalinity of the water). Please have this in mind when rating the measured values for ammonium/ammonia.
Practically, ready-to-use test kits can be used the best to measure
the necessary
parameter. There are test kits available e.g. from the
company JBL which are quick and easy-to-use, even under field
conditions (example for
ammonia measurements (for more information at their website scan the QR-code
at the left with your smartphone).

The choice of test kits covers almost any kind of interesting parameter, even oxygen and pH can be measured with these kits. However, for daily oxygen and pH measurements, a durable probe is more appropriate, but needs a significant one-time investment. An instrument which measures dissolved oxygen and oxygen saturation according to temperature is known under the brand name "Oxyguard" and is one of the best and robust equipment under field conditions, but quite expensive.
JBL-Testkits
Using the test kits of e.g. JBL to measure water parameter is quite easy. The principle is a reaction among the parameter to measure (e.g. ammonia in the water) and one or two reagents which produce a certain color in the sample after a given time. All the necessary equipment comes with the test kits (small glasses for the samples, spoon for powdered reagents, syringe and a colour card, which is being used then used to compare with a blank.
This table indicates the wide variety of parameters which can easily be measured, using the test kits of JBL.
 Usually, two small glass vials are needed for a measurement. Both
vials are filled with the water sample. In one vial reagents are
added according to the manufacturers advices and then some time is
needed to develop the reaction (the color).
Usually, two small glass vials are needed for a measurement. Both
vials are filled with the water sample. In one vial reagents are
added according to the manufacturers advices and then some time is
needed to develop the reaction (the color).
After 3-5 minutes, the color is fully developed and the comparison with the coulor code card (see figure below) can be accomplished. The precision of these test kits is mostly sufficient even in a professional hatchery environment. The example below shows the color card for the measurement of NH4 – NH3.
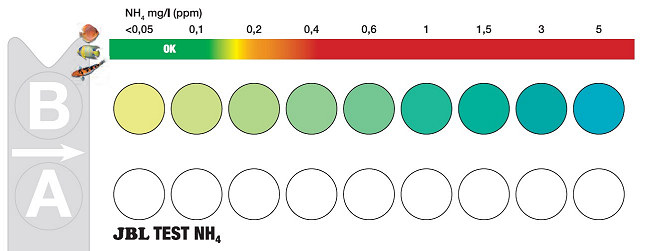
The blank has to cover the coloured spots, the sample the white spots. The color card provides an estimation about the save range (on top) concerning the measured parameter. Please note that these values are related to pet fish environment; safe values for commercial aquaculture may differ from this recommendation (e.g. for NH4 – NH3 values in the hatchery are safe until about 0.7-0.9 mg/l, compare with the Table above).

After the given time, the tray with the two vials gas has to be
placed on the related color card (for each parameter, a specific
color card is available). The blank is put on the coloured spots,
the sample on the white spots. Move the tray to the position where
both vials show the same color and read the value. Each color
card provides a recommendation for a safe range.
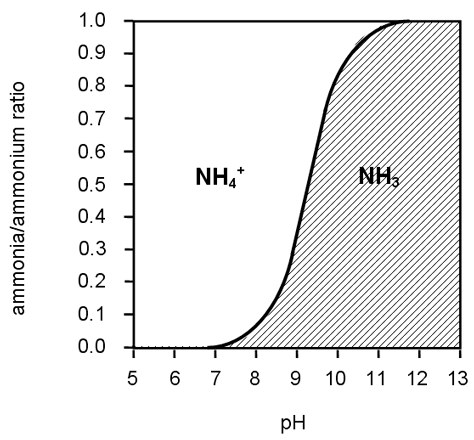
Ammonia and ammonium are different forms of nitrogen. The major factor that determines the proportion of ammonia to ammonium in water is the pH. The activity of the ammonia is also influenced by ionic strength and temperature. It is important to remember as unionized NH3 can be harmful to aquatic organisms, while ionized ammonium is basically harmless.
The chemical equation that drives the relationship between ammonia and ammonium is:
NH3 + H2O <-> NH4 + + OH -
When the pH is low, the reaction is driven to the right, and when the pH is high, the reaction is driven to the left. In general, at a temperature of around room temperature, at a pH less than 6.0, the proportion of ammonium-N plus ammonia-N as NH3 is very very low and as NH4+ is very high. At a pH around 8.0, the proportion as NH3 is 10 percent or less, and at a pH slightly above 9.0, the proportion is about 50 percent.
The activity of aqueous ammonia also is much lower at low temperatures and higher at warm temperatures. This means that at low temperatures and low pH the activity as NH3 is even lower, and as NH4+ is even higher. Once the pH is > 11, all ammonium-N ions in solution will be converted to ammonia-N. When you test for ammonia with your test kit, the reading you actually have is a combination of ammonium (NH4+ or ionized ammonia) and ammonia (NH3 or unionized ammonia) known as Total Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN). Ammonia is the toxic part of the TAN. Ammonium, even at high concentrations, does not cause mortality in fish. Please note, however, that a "normal" pH in the hatchery will be between 7-8.
Costs for JBL-Testkits:
A complete case with test kits for 11 parameters is about 75 Euro. Recommended as the basic kit, since it comes with all necessary equipment (glasses for samples, glass tray, syringe, spoon, color cards and instruction manual. For further use, only replacement kits are necessary. Following some examples for replacements.
- Replacement kit NH4 – NH3:c.a. 6 Euro (about 50 measurements)
- Replacement kit NO3: c.a. 8 Euro (about 50 measurements)
- Replacement kit NO2: c.a. 6 Euro (about 50 measurements)